/README.md
https://gitlab.com/jforge/reveal.js · Markdown · 1014 lines · 711 code · 303 blank · 0 comment · 0 complexity · 639637146669111fd5036b59a39593a4 MD5 · raw file
- # reveal.js [](https://travis-ci.org/hakimel/reveal.js)
- A framework for easily creating beautiful presentations using HTML. [Check out the live demo](http://lab.hakim.se/reveal-js/).
- reveal.js comes with a broad range of features including [nested slides](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js#markup), [Markdown contents](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js#markdown), [PDF export](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js#pdf-export), [speaker notes](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js#speaker-notes) and a [JavaScript API](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js#api). It's best viewed in a modern browser but [fallbacks](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/wiki/Browser-Support) are available to make sure your presentation can still be viewed elsewhere.
- #### More reading:
- - [Installation](#installation): Step-by-step instructions for getting reveal.js running on your computer.
- - [Changelog](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/releases): Up-to-date version history.
- - [Examples](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/wiki/Example-Presentations): Presentations created with reveal.js, add your own!
- - [Browser Support](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/wiki/Browser-Support): Explanation of browser support and fallbacks.
- - [Plugins](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/wiki/Plugins,-Tools-and-Hardware): A list of plugins that can be used to extend reveal.js.
- ## Online Editor
- Presentations are written using HTML or Markdown but there's also an online editor for those of you who prefer a graphical interface. Give it a try at [http://slides.com](http://slides.com).
- ## Instructions
- ### Markup
- Markup hierarchy needs to be ``<div class="reveal"> <div class="slides"> <section>`` where the ``<section>`` represents one slide and can be repeated indefinitely. If you place multiple ``<section>``'s inside of another ``<section>`` they will be shown as vertical slides. The first of the vertical slides is the "root" of the others (at the top), and it will be included in the horizontal sequence. For example:
- ```html
- <div class="reveal">
- <div class="slides">
- <section>Single Horizontal Slide</section>
- <section>
- <section>Vertical Slide 1</section>
- <section>Vertical Slide 2</section>
- </section>
- </div>
- </div>
- ```
- ### Markdown
- It's possible to write your slides using Markdown. To enable Markdown, add the ```data-markdown``` attribute to your ```<section>``` elements and wrap the contents in a ```<script type="text/template">``` like the example below.
- This is based on [data-markdown](https://gist.github.com/1343518) from [Paul Irish](https://github.com/paulirish) modified to use [marked](https://github.com/chjj/marked) to support [Github Flavoured Markdown](https://help.github.com/articles/github-flavored-markdown). Sensitive to indentation (avoid mixing tabs and spaces) and line breaks (avoid consecutive breaks).
- ```html
- <section data-markdown>
- <script type="text/template">
- ## Page title
- A paragraph with some text and a [link](http://hakim.se).
- </script>
- </section>
- ```
- #### External Markdown
- You can write your content as a separate file and have reveal.js load it at runtime. Note the separator arguments which determine how slides are delimited in the external file. The ```data-charset``` attribute is optional and specifies which charset to use when loading the external file.
- When used locally, this feature requires that reveal.js [runs from a local web server](#full-setup).
- ```html
- <section data-markdown="example.md"
- data-separator="^\n\n\n"
- data-separator-vertical="^\n\n"
- data-separator-notes="^Note:"
- data-charset="iso-8859-15">
- </section>
- ```
- #### Element Attributes
- Special syntax (in html comment) is available for adding attributes to Markdown elements. This is useful for fragments, amongst other things.
- ```html
- <section data-markdown>
- <script type="text/template">
- - Item 1 <!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="2" -->
- - Item 2 <!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1" -->
- </script>
- </section>
- ```
- #### Slide Attributes
- Special syntax (in html comment) is available for adding attributes to the slide `<section>` elements generated by your Markdown.
- ```html
- <section data-markdown>
- <script type="text/template">
- <!-- .slide: data-background="#ff0000" -->
- Markdown content
- </script>
- </section>
- ```
- ### Configuration
- At the end of your page you need to initialize reveal by running the following code. Note that all config values are optional and will default as specified below.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- // Display controls in the bottom right corner
- controls: true,
- // Display a presentation progress bar
- progress: true,
- // Display the page number of the current slide
- slideNumber: false,
- // Push each slide change to the browser history
- history: false,
- // Enable keyboard shortcuts for navigation
- keyboard: true,
- // Enable the slide overview mode
- overview: true,
- // Vertical centering of slides
- center: true,
- // Enables touch navigation on devices with touch input
- touch: true,
- // Loop the presentation
- loop: false,
- // Change the presentation direction to be RTL
- rtl: false,
- // Turns fragments on and off globally
- fragments: true,
- // Flags if the presentation is running in an embedded mode,
- // i.e. contained within a limited portion of the screen
- embedded: false,
- // Flags if we should show a help overlay when the questionmark
- // key is pressed
- help: true,
- // Number of milliseconds between automatically proceeding to the
- // next slide, disabled when set to 0, this value can be overwritten
- // by using a data-autoslide attribute on your slides
- autoSlide: 0,
- // Stop auto-sliding after user input
- autoSlideStoppable: true,
- // Enable slide navigation via mouse wheel
- mouseWheel: false,
- // Hides the address bar on mobile devices
- hideAddressBar: true,
- // Opens links in an iframe preview overlay
- previewLinks: false,
- // Transition style
- transition: 'default', // none/fade/slide/convex/concave/zoom
- // Transition speed
- transitionSpeed: 'default', // default/fast/slow
- // Transition style for full page slide backgrounds
- backgroundTransition: 'default', // none/fade/slide/convex/concave/zoom
- // Number of slides away from the current that are visible
- viewDistance: 3,
- // Parallax background image
- parallaxBackgroundImage: '', // e.g. "'https://s3.amazonaws.com/hakim-static/reveal-js/reveal-parallax-1.jpg'"
- // Parallax background size
- parallaxBackgroundSize: '' // CSS syntax, e.g. "2100px 900px"
- });
- ```
- The configuration can be updated after initialization using the ```configure``` method:
- ```javascript
- // Turn autoSlide off
- Reveal.configure({ autoSlide: 0 });
- // Start auto-sliding every 5s
- Reveal.configure({ autoSlide: 5000 });
- ```
- ### Dependencies
- Reveal.js doesn't _rely_ on any third party scripts to work but a few optional libraries are included by default. These libraries are loaded as dependencies in the order they appear, for example:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- dependencies: [
- // Cross-browser shim that fully implements classList - https://github.com/eligrey/classList.js/
- { src: 'lib/js/classList.js', condition: function() { return !document.body.classList; } },
- // Interpret Markdown in <section> elements
- { src: 'plugin/markdown/marked.js', condition: function() { return !!document.querySelector( '[data-markdown]' ); } },
- { src: 'plugin/markdown/markdown.js', condition: function() { return !!document.querySelector( '[data-markdown]' ); } },
- // Syntax highlight for <code> elements
- { src: 'plugin/highlight/highlight.js', async: true, callback: function() { hljs.initHighlightingOnLoad(); } },
- // Zoom in and out with Alt+click
- { src: 'plugin/zoom-js/zoom.js', async: true },
- // Speaker notes
- { src: 'plugin/notes/notes.js', async: true },
- // Remote control your reveal.js presentation using a touch device
- { src: 'plugin/remotes/remotes.js', async: true },
- // MathJax
- { src: 'plugin/math/math.js', async: true }
- ]
- });
- ```
- You can add your own extensions using the same syntax. The following properties are available for each dependency object:
- - **src**: Path to the script to load
- - **async**: [optional] Flags if the script should load after reveal.js has started, defaults to false
- - **callback**: [optional] Function to execute when the script has loaded
- - **condition**: [optional] Function which must return true for the script to be loaded
- ### Ready Event
- A 'ready' event is fired when reveal.js has loaded all non-async dependencies and is ready to start navigating. To check if reveal.js is already 'ready' you can call `Reveal.isReady()`.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'ready', function( event ) {
- // event.currentSlide, event.indexh, event.indexv
- } );
- ```
- ### Presentation Size
- All presentations have a normal size, that is the resolution at which they are authored. The framework will automatically scale presentations uniformly based on this size to ensure that everything fits on any given display or viewport.
- See below for a list of configuration options related to sizing, including default values:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- ...
- // The "normal" size of the presentation, aspect ratio will be preserved
- // when the presentation is scaled to fit different resolutions. Can be
- // specified using percentage units.
- width: 960,
- height: 700,
- // Factor of the display size that should remain empty around the content
- margin: 0.1,
- // Bounds for smallest/largest possible scale to apply to content
- minScale: 0.2,
- maxScale: 1.5
- });
- ```
- ### Auto-sliding
- Presentations can be configure to progress through slides automatically, without any user input. To enable this you will need to tell the framework how many milliseconds it should wait between slides:
- ```javascript
- // Slide every five seconds
- Reveal.configure({
- autoSlide: 5000
- });
- ```
- When this is turned on a control element will appear that enables users to pause and resume auto-sliding. Alternatively, sliding can be paused or resumed by pressing »a« on the keyboard. Sliding is paused automatically as soon as the user starts navigating. You can disable these controls by specifying ```autoSlideStoppable: false``` in your reveal.js config.
- You can also override the slide duration for individual slides and fragments by using the ```data-autoslide``` attribute:
- ```html
- <section data-autoslide="2000">
- <p>After 2 seconds the first fragment will be shown.</p>
- <p class="fragment" data-autoslide="10000">After 10 seconds the next fragment will be shown.</p>
- <p class="fragment">Now, the fragment is displayed for 2 seconds before the next slide is shown.</p>
- </section>
- ```
- Whenever the auto-slide mode is resumed or paused the ```autoslideresumed``` and ```autoslidepaused``` events are fired.
- ### Keyboard Bindings
- If you're unhappy with any of the default keyboard bindings you can override them using the ```keyboard``` config option:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.configure({
- keyboard: {
- 13: 'next', // go to the next slide when the ENTER key is pressed
- 27: function() {}, // do something custom when ESC is pressed
- 32: null // don't do anything when SPACE is pressed (i.e. disable a reveal.js default binding)
- }
- });
- ```
- ### Lazy Loading
- When working on presentation with a lot of media or iframe content it's important to load lazily. Lazy loading means that reveal.js will only load content for the few slides nearest to the current slide. The number of slides that are preloaded is determined by the `viewDistance` configuration option.
- To enable lazy loading all you need to do is change your "src" attributes to "data-src" as shown below. This is supported for image, video, audio and iframe elements.
- ```html
- <section>
- <img data-src="image.png">
- <iframe data-src="http://slides.com"></iframe>
- <video>
- <source data-src="video.webm" type="video/webm" />
- <source data-src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
- </video>
- </section>
- ```
- ### API
- The ``Reveal`` object exposes a JavaScript API for controlling navigation and reading state:
- ```javascript
- // Navigation
- Reveal.slide( indexh, indexv, indexf );
- Reveal.left();
- Reveal.right();
- Reveal.up();
- Reveal.down();
- Reveal.prev();
- Reveal.next();
- Reveal.prevFragment();
- Reveal.nextFragment();
- // Toggle presentation states, optionally pass true/false to force on/off
- Reveal.toggleOverview();
- Reveal.togglePause();
- Reveal.toggleAutoSlide();
- // Change a config value at runtime
- Reveal.configure({ controls: true });
- // Returns the present configuration options
- Reveal.getConfig();
- // Fetch the current scale of the presentation
- Reveal.getScale();
- // Retrieves the previous and current slide elements
- Reveal.getPreviousSlide();
- Reveal.getCurrentSlide();
- Reveal.getIndices(); // { h: 0, v: 0 } }
- Reveal.getProgress(); // 0-1
- Reveal.getTotalSlides();
- // State checks
- Reveal.isFirstSlide();
- Reveal.isLastSlide();
- Reveal.isOverview();
- Reveal.isPaused();
- Reveal.isAutoSliding();
- ```
- ### Slide Changed Event
- A 'slidechanged' event is fired each time the slide is changed (regardless of state). The event object holds the index values of the current slide as well as a reference to the previous and current slide HTML nodes.
- Some libraries, like MathJax (see [#226](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/issues/226#issuecomment-10261609)), get confused by the transforms and display states of slides. Often times, this can be fixed by calling their update or render function from this callback.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'slidechanged', function( event ) {
- // event.previousSlide, event.currentSlide, event.indexh, event.indexv
- } );
- ```
- ### Presentation State
- The presentation's current state can be fetched by using the `getState` method. A state object contains all of the information required to put the presentation back as it was when `getState` was first called. Sort of like a snapshot. It's a simple object that can easily be stringified and persisted or sent over the wire.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.slide( 1 );
- // we're on slide 1
- var state = Reveal.getState();
- Reveal.slide( 3 );
- // we're on slide 3
- Reveal.setState( state );
- // we're back on slide 1
- ```
- ### Slide States
- If you set ``data-state="somestate"`` on a slide ``<section>``, "somestate" will be applied as a class on the document element when that slide is opened. This allows you to apply broad style changes to the page based on the active slide.
- Furthermore you can also listen to these changes in state via JavaScript:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'somestate', function() {
- // TODO: Sprinkle magic
- }, false );
- ```
- ### Slide Backgrounds
- Slides are contained within a limited portion of the screen by default to allow them to fit any display and scale uniformly. You can apply full page backgrounds outside of the slide area by adding a ```data-background``` attribute to your ```<section>``` elements. Four different types of backgrounds are supported: color, image, video and iframe. Below are a few examples.
- ```html
- <section data-background="#ff0000">
- <h2>All CSS color formats are supported, like rgba() or hsl().</h2>
- </section>
- <section data-background="http://example.com/image.png">
- <h2>This slide will have a full-size background image.</h2>
- </section>
- <section data-background="http://example.com/image.png" data-background-size="100px" data-background-repeat="repeat">
- <h2>This background image will be sized to 100px and repeated.</h2>
- </section>
- <section data-background-video="https://s3.amazonaws.com/static.slid.es/site/homepage/v1/homepage-video-editor.mp4,https://s3.amazonaws.com/static.slid.es/site/homepage/v1/homepage-video-editor.webm">
- <h2>Video. Multiple sources can be defined using a comma separated list.</h2>
- </section>
- <section data-background-iframe="https://slides.com">
- <h2>Embeds a web page as a background. Note that the page won't be interactive.</h2>
- </section>
- ```
- Backgrounds transition using a fade animation by default. This can be changed to a linear sliding transition by passing ```backgroundTransition: 'slide'``` to the ```Reveal.initialize()``` call. Alternatively you can set ```data-background-transition``` on any section with a background to override that specific transition.
- ### Parallax Background
- If you want to use a parallax scrolling background, set the two following config properties when initializing reveal.js (the third one is optional).
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- // Parallax background image
- parallaxBackgroundImage: '', // e.g. "https://s3.amazonaws.com/hakim-static/reveal-js/reveal-parallax-1.jpg"
- // Parallax background size
- parallaxBackgroundSize: '', // CSS syntax, e.g. "2100px 900px" - currently only pixels are supported (don't use % or auto)
- // This slide transition gives best results:
- transition: 'slide'
- });
- ```
- Make sure that the background size is much bigger than screen size to allow for some scrolling. [View example](http://lab.hakim.se/reveal-js/?parallaxBackgroundImage=https%3A%2F%2Fs3.amazonaws.com%2Fhakim-static%2Freveal-js%2Freveal-parallax-1.jpg¶llaxBackgroundSize=2100px%20900px).
- ### Slide Transitions
- The global presentation transition is set using the ```transition``` config value. You can override the global transition for a specific slide by using the ```data-transition``` attribute:
- ```html
- <section data-transition="zoom">
- <h2>This slide will override the presentation transition and zoom!</h2>
- </section>
- <section data-transition-speed="fast">
- <h2>Choose from three transition speeds: default, fast or slow!</h2>
- </section>
- ```
- Note that this does not work with the page and cube transitions.
- ### Internal links
- It's easy to link between slides. The first example below targets the index of another slide whereas the second targets a slide with an ID attribute (```<section id="some-slide">```):
- ```html
- <a href="#/2/2">Link</a>
- <a href="#/some-slide">Link</a>
- ```
- You can also add relative navigation links, similar to the built in reveal.js controls, by appending one of the following classes on any element. Note that each element is automatically given an ```enabled``` class when it's a valid navigation route based on the current slide.
- ```html
- <a href="#" class="navigate-left">
- <a href="#" class="navigate-right">
- <a href="#" class="navigate-up">
- <a href="#" class="navigate-down">
- <a href="#" class="navigate-prev"> <!-- Previous vertical or horizontal slide -->
- <a href="#" class="navigate-next"> <!-- Next vertical or horizontal slide -->
- ```
- ### Fragments
- Fragments are used to highlight individual elements on a slide. Every element with the class ```fragment``` will be stepped through before moving on to the next slide. Here's an example: http://lab.hakim.se/reveal-js/#/fragments
- The default fragment style is to start out invisible and fade in. This style can be changed by appending a different class to the fragment:
- ```html
- <section>
- <p class="fragment grow">grow</p>
- <p class="fragment shrink">shrink</p>
- <p class="fragment roll-in">roll-in</p>
- <p class="fragment fade-out">fade-out</p>
- <p class="fragment current-visible">visible only once</p>
- <p class="fragment highlight-current-blue">blue only once</p>
- <p class="fragment highlight-red">highlight-red</p>
- <p class="fragment highlight-green">highlight-green</p>
- <p class="fragment highlight-blue">highlight-blue</p>
- </section>
- ```
- Multiple fragments can be applied to the same element sequentially by wrapping it, this will fade in the text on the first step and fade it back out on the second.
- ```html
- <section>
- <span class="fragment fade-in">
- <span class="fragment fade-out">I'll fade in, then out</span>
- </span>
- </section>
- ```
- The display order of fragments can be controlled using the ```data-fragment-index``` attribute.
- ```html
- <section>
- <p class="fragment" data-fragment-index="3">Appears last</p>
- <p class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1">Appears first</p>
- <p class="fragment" data-fragment-index="2">Appears second</p>
- </section>
- ```
- ### Fragment events
- When a slide fragment is either shown or hidden reveal.js will dispatch an event.
- Some libraries, like MathJax (see #505), get confused by the initially hidden fragment elements. Often times this can be fixed by calling their update or render function from this callback.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'fragmentshown', function( event ) {
- // event.fragment = the fragment DOM element
- } );
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'fragmenthidden', function( event ) {
- // event.fragment = the fragment DOM element
- } );
- ```
- ### Code syntax highlighting
- By default, Reveal is configured with [highlight.js](http://softwaremaniacs.org/soft/highlight/en/) for code syntax highlighting. Below is an example with clojure code that will be syntax highlighted. When the `data-trim` attribute is present surrounding whitespace is automatically removed.
- ```html
- <section>
- <pre><code data-trim>
- (def lazy-fib
- (concat
- [0 1]
- ((fn rfib [a b]
- (lazy-cons (+ a b) (rfib b (+ a b)))) 0 1)))
- </code></pre>
- </section>
- ```
- ### Slide number
- If you would like to display the page number of the current slide you can do so using the ```slideNumber``` configuration value.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.configure({ slideNumber: true });
- ```
- ### Overview mode
- Press "Esc" or "o" keys to toggle the overview mode on and off. While you're in this mode, you can still navigate between slides,
- as if you were at 1,000 feet above your presentation. The overview mode comes with a few API hooks:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'overviewshown', function( event ) { /* ... */ } );
- Reveal.addEventListener( 'overviewhidden', function( event ) { /* ... */ } );
- // Toggle the overview mode programmatically
- Reveal.toggleOverview();
- ```
- ### Fullscreen mode
- Just press »F« on your keyboard to show your presentation in fullscreen mode. Press the »ESC« key to exit fullscreen mode.
- ### Embedded media
- Embedded HTML5 `<video>`/`<audio>` and YouTube iframes are automatically paused when you navigate away from a slide. This can be disabled by decorating your element with a `data-ignore` attribute.
- Add `data-autoplay` to your media element if you want it to automatically start playing when the slide is shown:
- ```html
- <video data-autoplay src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"></video>
- ```
- Additionally the framework automatically pushes two [post messages](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window.postMessage) to all iframes, ```slide:start``` when the slide containing the iframe is made visible and ```slide:stop``` when it is hidden.
- ### Stretching elements
- Sometimes it's desirable to have an element, like an image or video, stretch to consume as much space as possible within a given slide. This can be done by adding the ```.stretch``` class to an element as seen below:
- ```html
- <section>
- <h2>This video will use up the remaining space on the slide</h2>
- <video class="stretch" src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"></video>
- </section>
- ```
- Limitations:
- - Only direct descendants of a slide section can be stretched
- - Only one descendant per slide section can be stretched
- ### postMessage API
- The framework has a built-in postMessage API that can be used when communicating with a presentation inside of another window. Here's an example showing how you'd make a reveal.js instance in the given window proceed to slide 2:
- ```javascript
- <window>.postMessage( JSON.stringify({ method: 'slide', args: [ 2 ] }), '*' );
- ```
- When reveal.js runs inside of an iframe it can optionally bubble all of its events to the parent. Bubbled events are stringified JSON with three fields: namespace, eventName and state. Here's how you subscribe to them from the parent window:
- ```javascript
- window.addEventListener( 'message', function( event ) {
- var data = JSON.parse( event.data );
- if( data.namespace === 'reveal' && data.eventName ='slidechanged' ) {
- // Slide changed, see data.state for slide number
- }
- } );
- ```
- This cross-window messaging can be toggled on or off using configuration flags.
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- ...,
- // Exposes the reveal.js API through window.postMessage
- postMessage: true,
- // Dispatches all reveal.js events to the parent window through postMessage
- postMessageEvents: false
- });
- ```
- ## PDF Export
- Presentations can be exported to PDF via a special print stylesheet. This feature requires that you use [Google Chrome](http://google.com/chrome).
- Here's an example of an exported presentation that's been uploaded to SlideShare: http://www.slideshare.net/hakimel/revealjs-300.
- 1. Open your presentation with `print-pdf` included anywhere in the query string. This triggers the default index HTML to load the PDF print stylesheet ([css/print/pdf.css](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/blob/master/css/print/pdf.css)). You can test this with [lab.hakim.se/reveal-js?print-pdf](http://lab.hakim.se/reveal-js?print-pdf).
- 2. Open the in-browser print dialog (CMD+P).
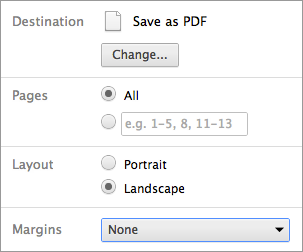
- 3. Change the **Destination** setting to **Save as PDF**.
- 4. Change the **Layout** to **Landscape**.
- 5. Change the **Margins** to **None**.
- 6. Click **Save**.
- 
- ## Theming
- The framework comes with a few different themes included:
- - black: Black background, white text, blue links (default theme)
- - white: White background, black text, blue links
- - league: Gray background, white text, blue links (default theme for reveal.js < 3.0.0)
- - beige: Beige background, dark text, brown links
- - sky: Blue background, thin white text, blue links
- - night: Black background, thick white text, orange links
- - serif: Cappuccino background, gray text, brown links
- - simple: White background, black text, blue links
- - solarized: Cream-colored background, dark green text, blue links
- Each theme is available as a separate stylesheet. To change theme you will need to replace **black** below with your desired theme name in index.html:
- ```html
- <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/theme/black.css" id="theme">
- ```
- If you want to add a theme of your own see the instructions here: [/css/theme/README.md](https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/blob/master/css/theme/README.md).
- ## Speaker Notes
- reveal.js comes with a speaker notes plugin which can be used to present per-slide notes in a separate browser window. The notes window also gives you a preview of the next upcoming slide so it may be helpful even if you haven't written any notes. Press the 's' key on your keyboard to open the notes window.
- Notes are defined by appending an ```<aside>``` element to a slide as seen below. You can add the ```data-markdown``` attribute to the aside element if you prefer writing notes using Markdown.
- When used locally, this feature requires that reveal.js [runs from a local web server](#full-setup).
- ```html
- <section>
- <h2>Some Slide</h2>
- <aside class="notes">
- Oh hey, these are some notes. They'll be hidden in your presentation, but you can see them if you open the speaker notes window (hit 's' on your keyboard).
- </aside>
- </section>
- ```
- If you're using the external Markdown plugin, you can add notes with the help of a special delimiter:
- ```html
- <section data-markdown="example.md" data-separator="^\n\n\n" data-separator-vertical="^\n\n" data-separator-notes="^Note:"></section>
- # Title
- ## Sub-title
- Here is some content...
- Note:
- This will only display in the notes window.
- ```
- ## Server Side Speaker Notes
- In some cases it can be desirable to run notes on a separate device from the one you're presenting on. The Node.js-based notes plugin lets you do this using the same note definitions as its client side counterpart. Include the required scripts by adding the following dependencies:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- ...
- dependencies: [
- { src: 'socket.io/socket.io.js', async: true },
- { src: 'plugin/notes-server/client.js', async: true }
- ]
- });
- ```
- Then:
- 1. Install [Node.js](http://nodejs.org/)
- 2. Run ```npm install```
- 3. Run ```node plugin/notes-server```
- ## Multiplexing
- The multiplex plugin allows your audience to view the slides of the presentation you are controlling on their own phone, tablet or laptop. As the master presentation navigates the slides, all client presentations will update in real time. See a demo at [http://revealjs.jit.su/](http://revealjs.jit.su).
- The multiplex plugin needs the following 3 things to operate:
- 1. Master presentation that has control
- 2. Client presentations that follow the master
- 3. Socket.io server to broadcast events from the master to the clients
- More details:
- #### Master presentation
- Served from a static file server accessible (preferably) only to the presenter. This need only be on your (the presenter's) computer. (It's safer to run the master presentation from your own computer, so if the venue's Internet goes down it doesn't stop the show.) An example would be to execute the following commands in the directory of your master presentation:
- 1. ```npm install node-static```
- 2. ```static```
- If you want to use the speaker notes plugin with your master presentation then make sure you have the speaker notes plugin configured correctly along with the configuration shown below, then execute ```node plugin/notes-server``` in the directory of your master presentation. The configuration below will cause it to connect to the socket.io server as a master, as well as launch your speaker-notes/static-file server.
- You can then access your master presentation at ```http://localhost:1947```
- Example configuration:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- // other options...
- multiplex: {
- // Example values. To generate your own, see the socket.io server instructions.
- secret: '13652805320794272084', // Obtained from the socket.io server. Gives this (the master) control of the presentation
- id: '1ea875674b17ca76', // Obtained from socket.io server
- url: 'revealjs.jit.su:80' // Location of socket.io server
- },
- // Don't forget to add the dependencies
- dependencies: [
- { src: '//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/socket.io/0.9.16/socket.io.min.js', async: true },
- { src: 'plugin/multiplex/master.js', async: true },
- // and if you want speaker notes
- { src: 'plugin/notes-server/client.js', async: true }
- // other dependencies...
- ]
- });
- ```
- #### Client presentation
- Served from a publicly accessible static file server. Examples include: GitHub Pages, Amazon S3, Dreamhost, Akamai, etc. The more reliable, the better. Your audience can then access the client presentation via ```http://example.com/path/to/presentation/client/index.html```, with the configuration below causing them to connect to the socket.io server as clients.
- Example configuration:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- // other options...
- multiplex: {
- // Example values. To generate your own, see the socket.io server instructions.
- secret: null, // null so the clients do not have control of the master presentation
- id: '1ea875674b17ca76', // id, obtained from socket.io server
- url: 'revealjs.jit.su:80' // Location of socket.io server
- },
- // Don't forget to add the dependencies
- dependencies: [
- { src: '//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/socket.io/0.9.16/socket.io.min.js', async: true },
- { src: 'plugin/multiplex/client.js', async: true }
- // other dependencies...
- ]
- });
- ```
- #### Socket.io server
- Server that receives the slideChanged events from the master presentation and broadcasts them out to the connected client presentations. This needs to be publicly accessible. You can run your own socket.io server with the commands:
- 1. ```npm install```
- 2. ```node plugin/multiplex```
- Or you use the socket.io server at [http://revealjs.jit.su](http://revealjs.jit.su).
- You'll need to generate a unique secret and token pair for your master and client presentations. To do so, visit ```http://example.com/token```, where ```http://example.com``` is the location of your socket.io server. Or if you're going to use the socket.io server at [http://revealjs.jit.su](http://revealjs.jit.su), visit [http://revealjs.jit.su/token](http://revealjs.jit.su/token).
- You are very welcome to point your presentations at the Socket.io server running at [http://revealjs.jit.su](http://revealjs.jit.su), but availability and stability are not guaranteed. For anything mission critical I recommend you run your own server. It is simple to deploy to nodejitsu, heroku, your own environment, etc.
- ##### socket.io server as file static server
- The socket.io server can play the role of static file server for your client presentation, as in the example at [http://revealjs.jit.su](http://revealjs.jit.su). (Open [http://revealjs.jit.su](http://revealjs.jit.su) in two browsers. Navigate through the slides on one, and the other will update to match.)
- Example configuration:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- // other options...
- multiplex: {
- // Example values. To generate your own, see the socket.io server instructions.
- secret: null, // null so the clients do not have control of the master presentation
- id: '1ea875674b17ca76', // id, obtained from socket.io server
- url: 'example.com:80' // Location of your socket.io server
- },
- // Don't forget to add the dependencies
- dependencies: [
- { src: '//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/socket.io/0.9.16/socket.io.min.js', async: true },
- { src: 'plugin/multiplex/client.js', async: true }
- // other dependencies...
- ]
- ```
- It can also play the role of static file server for your master presentation and client presentations at the same time (as long as you don't want to use speaker notes). (Open [http://revealjs.jit.su](http://revealjs.jit.su) in two browsers. Navigate through the slides on one, and the other will update to match. Navigate through the slides on the second, and the first will update to match.) This is probably not desirable, because you don't want your audience to mess with your slides while you're presenting. ;)
- Example configuration:
- ```javascript
- Reveal.initialize({
- // other options...
- multiplex: {
- // Example values. To generate your own, see the socket.io server instructions.
- secret: '13652805320794272084', // Obtained from the socket.io server. Gives this (the master) control of the presentation
- id: '1ea875674b17ca76', // Obtained from socket.io server
- url: 'example.com:80' // Location of your socket.io server
- },
- // Don't forget to add the dependencies
- dependencies: [
- { src: '//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/socket.io/0.9.16/socket.io.min.js', async: true },
- { src: 'plugin/multiplex/master.js', async: true },
- { src: 'plugin/multiplex/client.js', async: true }
- // other dependencies...
- ]
- });
- ```
- ## Leap Motion
- The Leap Motion plugin lets you utilize your [Leap Motion](https://www.leapmotion.com/) device to control basic navigation of your presentation. The gestures currently supported are:
- ##### 1 to 2 fingers
- Pointer — Point to anything on screen. Move your finger past the device to expand the pointer.
- ##### 1 hand + 3 or more fingers (left/right/up/down)
- Navigate through your slides. See config options to invert movements.
- ##### 2 hands upwards
- Toggle the overview mode. Do it a second time to exit the overview.
- #### Config Options
- You can edit the following options:
- | Property | Default | Description
- | ----------------- |:-----------------:| :-------------
- | autoCenter | true | Center the pointer based on where you put your finger into the leap motions detection field.
- | gestureDelay | 500 | How long to delay between gestures in milliseconds.
- | naturalSwipe | true | Swipe as though you were touching a touch screen. Set to false to invert.
- | pointerColor | #00aaff | The color of the pointer.
- | pointerOpacity | 0.7 | The opacity of the pointer.
- | pointerSize | 15 | The minimum height and width of the pointer.
- | pointerTolerance | 120 | Bigger = slower pointer.
- Example configuration:
- ```js
- Reveal.initialize({
- // other options...
- leap: {
- naturalSwipe : false, // Invert swipe gestures
- pointerOpacity : 0.5, // Set pointer opacity to 0.5
- pointerColor : '#d80000' // Red pointer
- },
- dependencies: [
- { src: 'plugin/leap/leap.js', async: true }
- ]
- });
- ```
- ## MathJax
- If you want to display math equations in your presentation you can easily do so by including this plugin. The plugin is a very thin wrapper around the [MathJax](http://www.mathjax.org/) library. To use it you'll need to include it as a reveal.js dependency, [find our more about dependencies here](#dependencies).
- The plugin defaults to using [LaTeX](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LaTeX) but that can be adjusted through the ```math``` configuration object. Note that MathJax is loaded from a remote server. If you want to use it offline you'll need to download a copy of the library and adjust the ```mathjax``` configuration value.
- Below is an example of how the plugin can be configured. If you don't intend to change these values you do not need to include the ```math``` config object at all.
- ```js
- Reveal.initialize({
- // other options ...
- math: {
- mathjax: 'http://cdn.mathjax.org/mathjax/latest/MathJax.js',
- config: 'TeX-AMS_HTML-full' // See http://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/config-files.html
- },
-
- dependencies: [
- { src: 'plugin/math/math.js', async: true }
- ]
- });
- ```
- Read MathJax's documentation if you need [HTTPS delivery](http://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/start.html#secure-access-to-the-cdn) or serving of [specific versions](http://docs.mathjax.org/en/latest/configuration.html#loading-mathjax-from-the-cdn) for stability.
- ## Installation
- The **basic setup** is for authoring presentations only. The **full setup** gives you access to all reveal.js features and plugins such as speaker notes as well as the development tasks needed to make changes to the source.
- ### Basic setup
- The core of reveal.js is very easy to install. You'll simply need to download a copy of this repository and open the index.html file directly in your browser.
- 1. Download the latest version of reveal.js from <https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/releases>
- 2. Unzip and replace the example contents in index.html with your own
- 3. Open index.html in a browser to view it
- ### Full setup
- Some reveal.js features, like external Markdown and speaker notes, require that presentations run from a local web server. The following instructions will set up such a server as well as all of the development tasks needed to make edits to the reveal.js source code.
- 1. Install [Node.js](http://nodejs.org/)
- 2. Install [Grunt](http://gruntjs.com/getting-started#installing-the-cli)
- 4. Clone the reveal.js repository
- ```sh
- $ git clone https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js.git
- ```
- 5. Navigate to the reveal.js folder
- ```sh
- $ cd reveal.js
- ```
- 6. Install dependencies
- ```sh
- $ npm install
- ```
- 7. Serve the presentation and monitor source files for changes
- ```sh
- $ grunt serve
- ```
- 8. Open <http://localhost:8000> to view your presentation
- You can change the port by using `grunt serve --port 8001`.
- ### Folder Structure
- - **css/** Core styles without which the project does not function
- - **js/** Like above but for JavaScript
- - **plugin/** Components that have been developed as extensions to reveal.js
- - **lib/** All other third party assets (JavaScript, CSS, fonts)
- ## License
- MIT licensed
- Copyright (C) 2015 Hakim El Hattab, http://hakim.se